SENTINEL-1 L1 SLC TOPSAR Product Format Prototype
Example of slc TOPSAR product and some easy usage examples
Table of Contents¶
Introduction¶
In this notebook we will show an example of slc TOPSAR product and some easy usage examples
Objectives:
- Allow easy access to the bursts, since they are the data unit that is typically processed
- Provide ready-to-use datasets and data variable
- Allow users to open and manipulate data using both standard external tools and the EOPF
Relevant Features:
- Swaths, bursts and polarization are separeted in different products
- The coordinates associated to the data are the physical coordinates
- The zarr product will adhere to CF convetion (this will allow the user to open the prodoct with standards tools, such as xarray, exploiting properly the data coordinates).
- STAC attributes(Will be added in future)
Notes:
It is a preliminary example of product
- Not all the metadata are included in these product prototype, but they will be included in the future.
- Among the excluded metadata, there are:
- RFI
- qualityInformation
- downlinkInformation
- The stac attrabutes are still to be defined.
- The name of the variables are preliminary and they may change in the future.
- Variable attributes will be refined in the future, including:
- long_name
- units
- and standard names for coordinates
- The chunking is not defined yet.
- Products naming convention is to be defined.
- Reading from local and remote storage with EOPF is experimental(branch feat/coords_in_vars, commit 10a4f2e1) and not offically released.
%matplotlib inline
import datatree
import numpy as np
import xarray as xr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (10, 5)
plt.rcParams["font.size"] = 10swath = "IW1"
polarization = "VH"
burst_id = "249411"
zarr_name_1 = "S01SIWSLC_20231201T170634_0067_A117_S000_5464A_VH_IW1_249411"
zarr_name_2 = "S01SIWSLC_20231119T170635_0067_A117_S000_5464A_VH_IW1_249411"Remote files path
remote_product_path_1 = f"https://storage.sbg.cloud.ovh.net/v1/AUTH_8471d76cdd494d98a078f28b195dace4/sentinel-1-public/demo_product/slc/{zarr_name_1}.zarr/"
remote_product_path_2 = f"https://storage.sbg.cloud.ovh.net/v1/AUTH_8471d76cdd494d98a078f28b195dace4/sentinel-1-public/demo_product/slc/{zarr_name_2}.zarr/"Local files
The listed files do not work with the latest eopf-cpm library and therefore the next cells are commented out
# # Download the files into the folder ./scratch/demo_product/slc/
# !wget -q -r -nc -nH --cut-dirs=5 https://storage.sbg.cloud.ovh.net/v1/AUTH_8471d76cdd494d98a078f28b195dace4/sentinel-1-public/demo_product/slc --no-parent -P ./scratch/demo_product/slc/ --reject "index.html*"
# # Set the local product paths using the specified directory
# local_product_path_1 = f"./scratch/demo_product/slc/{zarr_name_1}.zarr/"
# local_product_path_2 = f"./scratch/demo_product/slc/{zarr_name_2}.zarr/"Read local files with EOPF¶
# store = EOZarrStore(local_product_path_1)
# store = store.open()
# store# store.load()Read remote files with xarray-datatree¶
(xarray extension that allow performing operations on hierachical structures)
dt = datatree.open_datatree(remote_product_path_1, engine="zarr", chunks={})
dtLoading...
burst = xr.open_dataset(remote_product_path_1, group="measurements", engine="zarr")[
"slc"
]
orbit = xr.open_dataset(remote_product_path_1, group="conditions/orbit", engine="zarr")orbit.plot.scatter(y="azimuth_time", x="position", hue="velocity", cmap="Blues")
plt.show()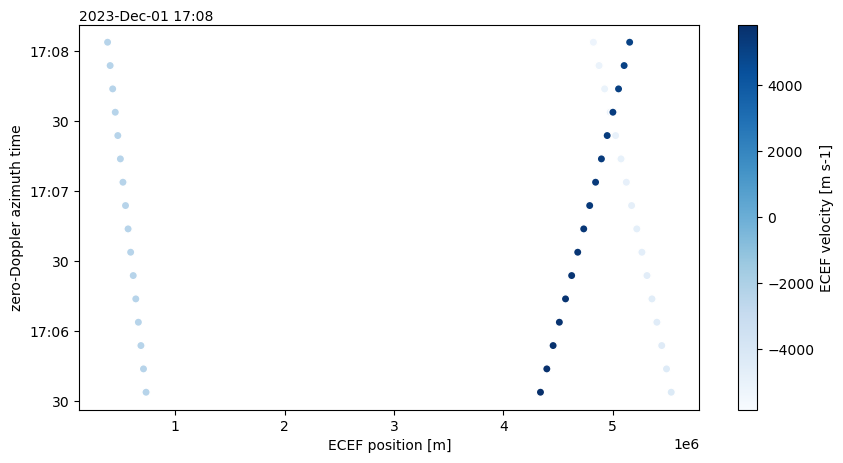
Interpolate
interp_orbit = orbit.interp_like(burst.azimuth_time)Plot
orbit.plot.scatter(y="azimuth_time", x="position", hue="velocity", cmap="Blues")
interp_orbit.plot.scatter(y="azimuth_time", x="position", color="red")
plt.show()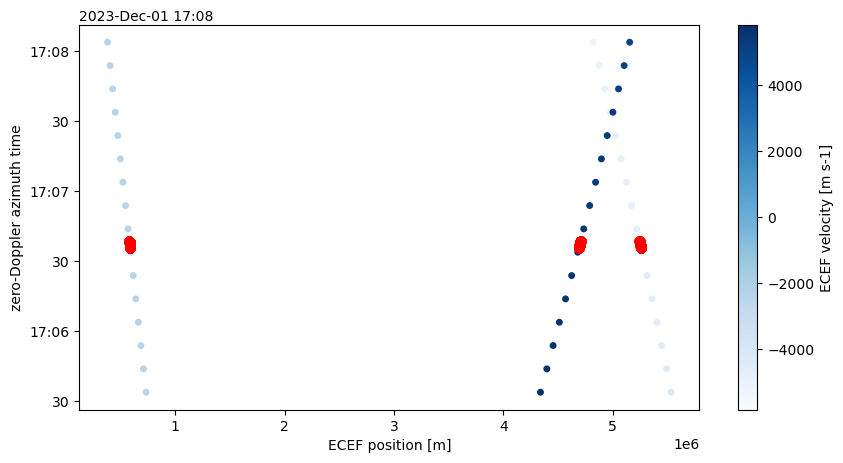
Calibration¶
Open Calibration lut data
calibration_lut = xr.open_dataset(
remote_product_path_1, group="quality/calibration", engine="zarr"
)Calibrate Data
calibration_matrix = calibration_lut.interp_like(burst)
calibrated_measurement = burst / calibration_matrix["sigma_nought"]Plot Full Data
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
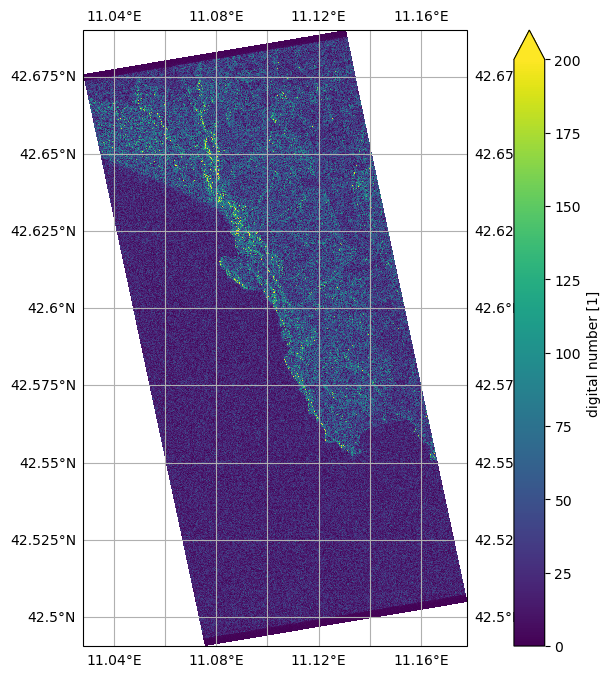
_ = abs(burst).plot(y="azimuth_time", vmax=200)Geocoding using GCPs¶
Open GCP Data
gcp = xr.open_dataset(remote_product_path_1, group="conditions/gcp", engine="zarr")Interpolate and assign new geographic coordinates
gcp_iterpolated = gcp.interp_like(burst)
burst = burst.assign_coords(
{"latitude": gcp_iterpolated.latitude, "longitude": gcp_iterpolated.longitude}
)Plot Subset
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
_, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": ccrs.Miller()}, figsize=(12, 8))
gl = ax.gridlines(
draw_labels=True, crs=ccrs.PlateCarree(), x_inline=False, y_inline=False
)
abs(burst[:, 7000:9000]).plot(
ax=ax, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(), x="longitude", y="latitude", vmax=200
)
plt.show()
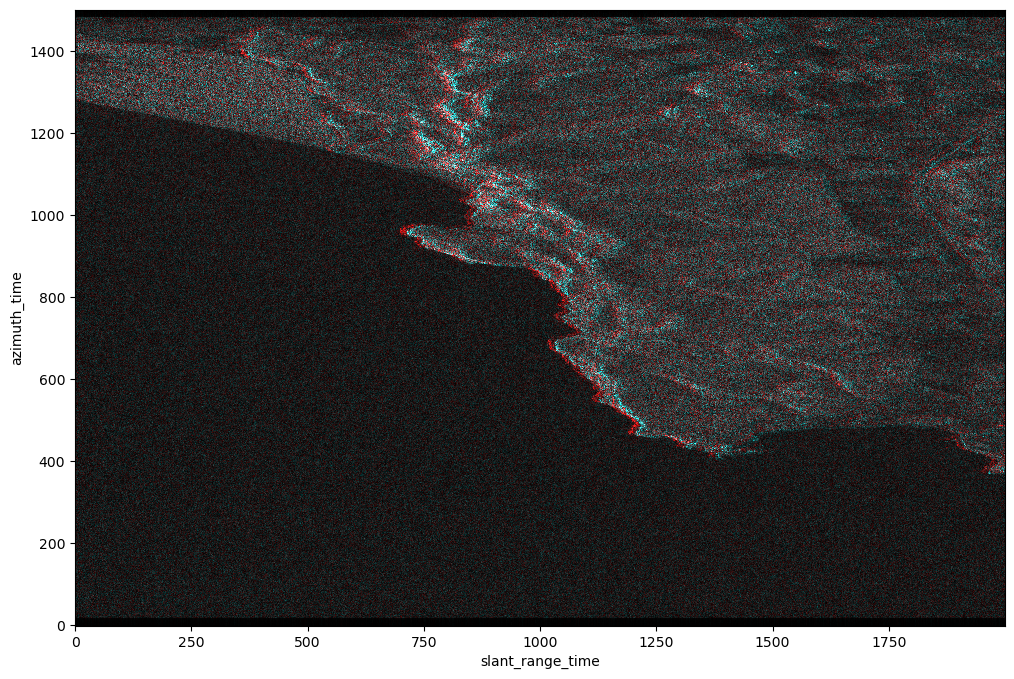
RGB Plot of two non coregistred burst¶
The RBG plot shows the shift between the non coregistred bursts
- swath:IW1
- polarization:VH
- burst_id:249411
- burst acquisition date:
- 2023-12-01
- 2023-11-19
Open Data
slc_1 = xr.open_dataset(remote_product_path_1, group="measurements", engine="zarr")[
"slc"
]
slc_2 = xr.open_dataset(remote_product_path_2, group="measurements", engine="zarr")[
"slc"
]
amp_1 = np.abs(slc_1).drop_vars(["azimuth_time", "slant_range_time"])
amp_2 = np.abs(slc_2).drop_vars(["azimuth_time", "slant_range_time"])Compose RGB
rgb = xr.concat([amp_1, amp_2, amp_2], dim="rgb")
rgb = xr.where(rgb > 200, 200, rgb) / 200Plot Subset
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
rgb[:, :, 7000:9000].plot.imshow(rgb="rgb")
plt.show()